| |
What is the flower?
A flower is a plant.
What is the main purpose of flowers?
A flower is the reproductive structure of a flowering plant, and as such its function is the production of seeds, which can grow into new plants, therefore assuring the survival of the species.
Flowers have leaf-like petals (which surround the reproductive parts of flowers). Petals usually have bright colours and scent, and they often bring insects and birds to pollinate the flowers.
Flowers may grow separately on the plant, or they may grow together in an inflorescence, which is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem.
Parts of a flower
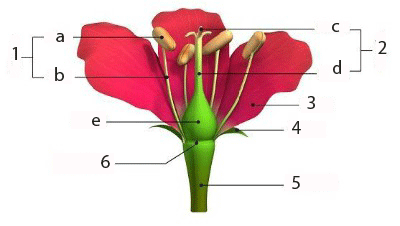
A complete flower has the following basic parts:
1. Stamen: the male reproductive organ of a flower, which has an anther (a.) and a stock or filament (b.).
The male reproductive parts of a flower are called the androecium.
2. Carpel: the female reproductive part of the flower, which has a stigma (c.), a style (d.) and an ovary (e.).
The female reproductive parts of a flower are called the gynoecium. Some flowers have both female and male parts, and some do not.
3. Petals: leaf-like structure which surrounds the reproductive parts of flowers. Petals usually have bright colours and scent, and they often bring insects and birds to pollinate the flowers.
Together, all of the petals of a flower are called a corolla.
4. Sepals: a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green and leaf-like, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom.
Together, the sepals form the calyx.
5. Pedicel: the stem that connects the flower to the plant and supports the entire structure of the flower, attaching a single flower to the inflorescence.
6. Receptacle: the part of a flower stalk where the parts of the flower are attached.
Types of flowers
Flowers have different classifications, according to the following characteristic:
1. Presence of reproductive organs:
- Hermaphrodite or monoecious: flowers that present the male and female reproductive organs in the same flower (callyx, corola, androecium and gynoecium), like tomatoes, hibiscus, roses.
- Dioecious: when the male and female reproductive organs occur in separate flowers, like holly, kiwi, cucumber, spinach.
2. Presence of floral elements:
- complete flowers: flowers that have all the floral elements: calyx, corolla, androecium, gynoecium, like roses, pea plants, tulips, lavender
- incomplete flowers: flowers where some floral elements are missing, like begonias, pumpkin, papaya, watermelon, bitter gourd, and corn.
Pollination
Pollination is the process that allows plants to reproduce through the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma.
In some cases, the wind and rain blow pollen between plants, which causes pollen to transfer to the female reproductive part of the plant; it is known as self pollination.
However, most plants need bees, butterflies, or other insects to pollinate from one plant to the next.
|
|




